Navigating product management: Essential skills, responsibilities, and tools
A product manager's dedication to planning, building, delivering, and iterating on solutions is what solves customer problems. Companies achieve sustainable success based on the strength of their offering. This is why product management continues to grow in influence and popularity. In 2022 for example, nearly 18 percent of MBA students at MIT Sloan School of Management accepted jobs in product management — making this the third-largest job category for graduates. Hiring site Glassdoor also ranks product management as the 10th best job in the United States for 2022.
The appeal of product management is particularly strong for those with an entrepreneurial spirit. Product managers are often able to operate with autonomy, work across many cross-functional groups, and develop lifelong career skills. The opportunity to make a meaningful impact on business growth and guide the product development process are also reasons that product management is such an in-demand discipline.
Product managers really, really love Aha! Roadmaps. Start a free trial.
Feel free to skip ahead to any of the following sections to learn more about product management:
What is product management?
Product management is responsible for delivering products and services that make customers happy and drive business growth. It is integral to a company's broader product development cycle — the entire process of transforming a raw idea into a solution that addresses customer needs, then measuring its success in the market.
Why is product management important?
If you are reading this, we bet you already know how important product management is to a business. But for folks outside of the field, how do you describe its essential nature?
Product managers build products that can make incredibly positive impacts in the lives of customers. You have the chance to create something new that solves customer problems and drives business growth and success.
Product building is a cross-functional endeavor — product management sits at the center. Product managers act as a bridge between engineering, design, marketing, sales, and customer support teams. You facilitate communication and ensure everyone works towards a common goal. From understanding customer needs and setting strategy to maximizing product value and market success, product management is the driving force behind it all.

Product management vs. project management
Understanding the differences between product and project management can be challenging. In smaller and mid-size companies, the responsibilities of both can overlap — causing even more confusion. Here is a quick way to differentiate between the two.
A product is what a business delivers to a group of potential customers. It can be anything — a physical item, a service, or a piece of software. Product managers set the strategy, build the product roadmap, and prioritize the work that brings the whole product together. It is an ongoing effort as you are managing the entire lifecycle of the product from launch through its subsequent releases, iterations, etc.
A project is a plan. There is a defined start and end date with a series of activities outlined within that fixed timeframe. Project managers oversee this fixed project from beginning to end — helping to implement the strategy set by the product manager. A product manager decides on the product initiatives and features, while the project manager develops a timeline based on the resource needs and delivery risks involved.

Related:
Product management responsibilities
Product managers are responsible for overseeing product-related activities along every stage of the product lifecycle — product development, launch, growth, maturity, and decline. Specifically, you are responsible for the strategy, roadmap, and feature definition for a product or product line. Some product management positions also include product marketing, forecasting, and profit and loss responsibilities.
Product management spans from strategic objectives to tactical activities, including:
Setting a product vision and strategy that is differentiated and delivers unique value based on customer demands. This includes defining personas and analyzing market and competitive conditions.
Defining what the product team will deliver and the timeline for implementation. This includes creating a release plan, capturing actionable feedback and ideas, and prioritizing features.
Providing cross-functional leadership — most notably between engineering teams, sales and marketing, and support. A key aspect of this is communicating progress against the product roadmap and keeping everyone informed of updates.
Analyzing product success. This entails tracking product metrics such as customer usage and bounce rates to determine the success of your offering.
The example below is a business model template in Aha! Roadmaps. Strategic models like this are a way product managers can capture assumptions about your market, analyze the state of your business, and plan for new opportunities.
Related: What does a product manager do?
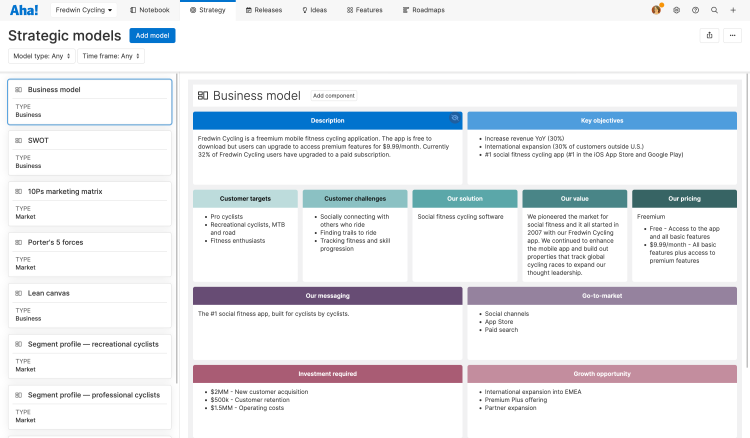
Use business models to further understand customer problems and the growth opportunities that exist within your market.
To better understand what product management entails, let's break down the responsibilities into internal and external spheres. Internal product management involves gathering customer research, competitive intelligence, and industry trends — as well as setting strategy and managing the product roadmap. External product management includes product marketing responsibilities such as messaging and branding, customer communication, new product launches, advertising, PR, and events. It is worth noting that product management and product marketing are typically separate roles, but there is frequent communication and close collaboration between them.
Product strategy and roadmap planning (Internal)
Customer interviews
Building product roadmaps
Go-to resource for the development team
Sales and support training
Product marketing and go-to-market activities (External)
Naming and branding
Customer communication
Press and analyst relations
Product manager skills
Product managers need a wide variety of skills to be successful. The best product managers are curious, thoughtful, compassionate, and organized. Each day, product managers work hard to align and drive action, maintaining a relentless focus on customer needs. You need a variety of skills to do this successfully — including working with UX designers to build wireframes and mockups, collaborating with engineering to scope out new features, and aligning with marketing to define the product messaging.
Some of the most important product management skills include:
Analytical skills
Communication
Empathy
Financial skills
Research
Technical skills (e.g., methodologies, processes, and tools)
Product management tools
Historically, most product managers simply used a combination of spreadsheets, presentations, and text documents to communicate their product strategy and roadmap. These tools are easily available and typically included in any company's suite of applications. But as the discipline evolved, it became clear there was a need for purpose-built product development tools — including roadmap software.
Now, cloud-based applications and SaaS tools make it possible to set strategy, ideate within digital notebooks and whiteboards, capture customer feedback, manage releases, define features, build visual product roadmaps, and analyze product success. These tools can also support teams that want to implement modern methodologies like agile product management.
Complete work and collaborate on product plans — try Aha! Roadmaps free for 30 days.
Unfortunately, the large number of product management apps that exist can make it difficult for product managers to work efficiently. Instead of having to switch between multiple tools for different purposes, it is smarter to consolidate them into one seamlessly integrated environment. This is why many product managers use the Aha! suite of tools. You can see an idea from conception to completion, collaborate with developers, and do all of your product planning and building in one place.
Careers in product management
Product management is a well-paid and rewarding career. Typically, product management titles range from the entry role of an associate product manager to a chief product officer who leads the entire product team.
Of course, specific titles and responsibilities depend on the company and the type of product you are building. For example, large organizations with multiple or complex offerings will likely have product portfolio managers to oversee their product lines. The methodology a company follows also matters — such as waterfall versus agile and kanban versus scrum. Your day-to-day role will vary based on the different workflows and processes of your company and team.

Product managers often transition into the role from all aspects of business — like engineering, marketing, sales, and customer service.
What is universal is that product management continues to expand as a profession. Demand for qualified product managers is growing at every level. If you are looking to start a career in product management, you can expect a challenging interview process. Be prepared to speak to your technical knowledge, decision-making skills, empathy, curiosity, and motivation. You can prepare for interviews by practicing from this comprehensive list of interview questions.
Types of product manager roles
There are several types of product manager roles out there — each with its own focus and responsibilities. Here are a few common examples:
Product manager: Manages the entire product lifecycle and roadmap
Product owner: Supports the development team
Growth product manager: Drives user and revenue growth
Technical product manager: Collaborates closely with engineering on product functionality
Platform product manager: Oversees components shared across multiple products
Product manager roles often stem from other positions in departments such as marketing, engineering, and project management. Your work in these previous positions heavily influences your ability and experience in product management. And in reality, the responsibilities and job titles can vary across different industries, companies, and product types. Some product managers may have a combination of these roles or specialize in specific domains — such as healthcare, finance, or e-commerce.
How to start a career in product management
Getting started in product management can come with a steep learning curve. Coursework and book study are great ways to develop foundational knowledge, but career success requires experience and skills acquired by actually being part of building and delivering products to customers.
Often times, product managers start their careers within a different department and then shift into this role. If you are currently working on a different team and are interested in becoming a product manager, make your interest known and watch for opportunities. In your role now, do everything you can to learn about the product and your customers. Reach out to people in your network in similar positions who could serve as a mentor as you prepare for this new and exciting career.
If you are just getting started in your career, keep in mind that most open product manager positions are not entry level. In your job search, look for titles including "associate product manager" or "product analyst". You can gain great experience in these kinds of positions — working towards a career in product management.
We have written extensively on this topic. Learn more from our career guides below:
Certifications for product managers
Demand for product managers has increased over the past decade — even as the role remains one that many professionals often stumble into and learn as they go. However, training programs and educational materials are quickly being offered and developed to support product managers who are looking to hone the craft.
For example, Aha! offers no-cost and fee-based courses to help product managers grow their skills. With Aha! Academy, you can receive in-depth training from our skilled instructors and earn certification in Aha! Roadmaps. Free, live tutorials are another good opportunity to learn best practices for using the Aha! suite from our team of product experts.
Learn more about the discipline of product management:
Frequently asked questions about product management
What is the purpose of product management?
The aim of product management is to deliver value to customers and the business. Specifically, product managers achieve this by defining a bold product vision and strategy, deeply understanding customers and the market, and leading the broader product team to make progress against the product roadmap. Building and delivering a product that customers love is the ultimate reward for all the great work that you do as a product manager.
What is product management not?
Many folks mistakenly conflate product management with project management. Product management is responsible for setting the product vision and strategy, defining the release process, and overseeing a product throughout its entire lifecycle. While product management is a strategic discipline, project management focuses more on the tactical details — resource planning, overseeing cross-functional dependencies, and making sure that deadlines are met.
Which roles support product management?
Product managers lead the cross-functional product team which typically includes representatives from innovation, product management, project management, product marketing, engineering, and operations. Beyond this core team, product management also works closely with members of marketing, sales, and support teams. Depending on the type of organization, product managers may also work closely with scrum masters, release managers, product operations managers, or technical product managers.
What is agile product management?
Inspired by agile software development methodologies, agile product management applies the principles of continuous improvement to the work of building and delivering products. Instead of planning products sequentially (and often slowly), agile product managers respond quickly to user feedback, collaborate closely with engineering, and release new customer experiences often. This agile approach allows for greater flexibility — you can continuously prioritize features and focus on delivering more value to customers.
Build products like you always wanted. See for yourself — start a free 30-day trial of Aha! software.